There are a few reason for Decision Making are made. They are:
*People need to analyse the amount of information
*People must make the decision quickly
*People must apply sophisticated analysis technique
*People must protect the corporate asset of organizational information.
Organizational level that you must know in an organization are start from EXECUTIVE as the highest level followed by the MANAGER and the lower level are the ANALYSIS.
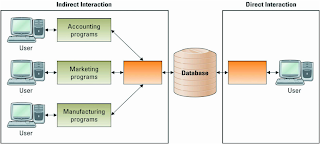
ONLINE TRANSACTION PROCESSING (OLTP)
* is the capturing of transaction and event information and event using the information according to define business rule.
TRANSACTION PROCESSING SYSTEM (TPS)
*the basic business system that serves the operational level in an organization.
ONLINE ANALYTICAL PROCESSING (OLAP)
*manipulation of information to create business intelligence in support of strategic decisin making.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE simulate the human intelligence such as the ability to reason and learn. There are many categories of artifiail intelligence which are :
- Expert system : computerized advisory programmed that imitiate the reasoning process of expert in solving difficult problem.
- Neural Network : attempt to emulate the way of human brain work.
- Generic Algorithm : mimics the evalution, survival-of-the fittest process to generate increasingly better solution to a problem.
- Intelligent Agent : special purpose knowledge-based information system that accomplished specific task on behalf of its user.
Thanks